What is Binding Energy?
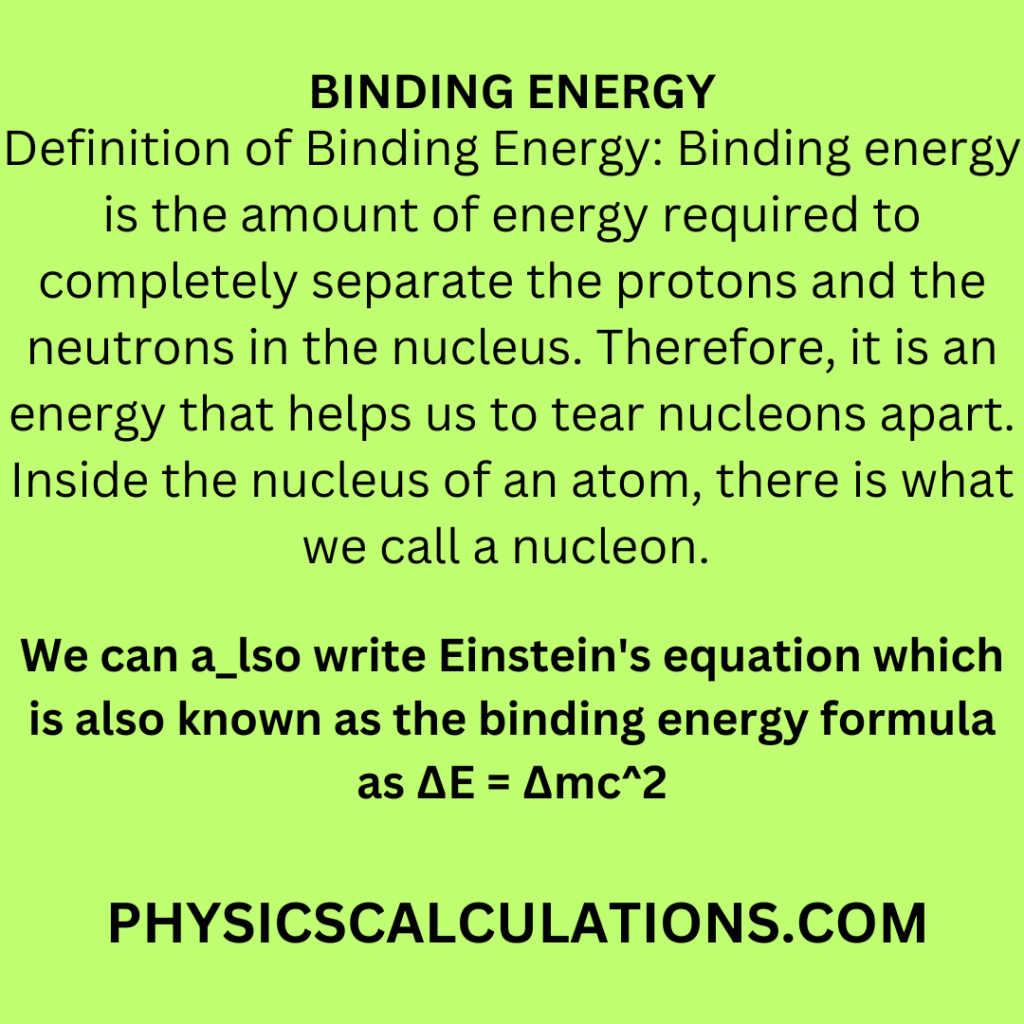
Definition of Binding Energy: Binding energy is the amount of energy required to completely separate the protons and the neutrons in the nucleus. Therefore, it is an energy that helps us to tear nucleons apart. Inside the nucleus of an atom, there is what we call a nucleon.
Nucleon are protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. The protons and neutrons (nucleons) are held together in the nucleus of an atom by very powerful nuclear forces. The amount of energy we need to separate those protons from neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is what we call binding energy.
Therefore, we need a very huge amount of energy to tear those nucleons apart. This energy is over 106 times more than that required to remove the electrons from an atom. Hence, when we separate the nucleus, it follows that the total mass is less than the mass of the nucleus. We also refer to the binding energy as the difference in mass or mass defect.
From the above explanation, we can now see that the binding energy of a nucleus is proportional to the difference between the total mass of the individual nucleons and the mass of the nucleons. Usually, the total mass of the stable nucleus or nuclide is less than the sum of the masses of its constituent nucleons.
Binding Energy Formula:
According to Albert Einstein, the difference in mass between all the individual nucleons and the mass of the nucleus is a measure of the binding energy. The energy released during the nuclear reaction (binding energy) is given by Einstein’s energy equation which is
E = mc2
We can also write Einstein’s equation which is also known as the binding energy formula as ΔE = Δmc2
Where
ΔE = Nuclear energy
Δm = change in mass
c = speed of light
The unit of energy in a nuclear reaction is in a unified atomic unit (u) or the electron volt (eV) or Joules (J). Here is how to convert the units:
Electron volt to Joule
1 eV = 1.6 x 10-19 J
Mega electron volt to Joules
1 MeV = 1.6 x 10-13 J
Atomic Unit to Joules
1 u = 931 MeV = 1.490 x 10-10 J
Mass Defect and Atomic Energy
Mass defect (Δm) can be defined as the mass of the element lost when a given mass of a radioactive atom is split into two parts. The formula for calculating mass defect is
Mass defect (Δm) = mass of the initial nucleus – total mass of the split part
Atomic energy is the energy released as a result of the splitting of a radioactive nucleus by fission or fusion.
How to Calculate Binding Energy
Here are a few problems that can help us to understand how to find binding energy:
Problem 1
In a nuclear reaction, the mass defect is 2.0 x 10-6 g. Calculate the energy released given that the velocity of light is 3.0 x 108 m/s.
Answer
The final answer to the above question is 1.8 x 108 J
Explanation
Data
Mass defect, m = 2.0 x 10-6 g = 2.0 x 10-9 kg
The velocity of light, c = 3.0 x 108 m/s
Unknown:
Energy, E = ?
Formula
E = mc2
Solution
E = mc2 = 2.0 x 10-9 x (3.0 x 108)2 = 1.8 x 108 J
Therefore, the energy released is 1.8 x 108 joules.
Problem 2
In a thermonuclear reaction, the total initial mass is 5.02 x 10-27 kilograms and the final mass is 5.01 x 10-27 kilograms. The energy released in the process is
Answer
The final answer to the above question is E = 9.0 x 10-13 J
Explanation
Data:
Initial mass, m1 = 5.02 x 10-27 kg
Final mass, m2 = 5.01 x 10-27 kg
Speed of light, c = 3 x 108 m/s
Unknown:
Mass defect, m = ?
Energy released, E = ?
Formula
Step 1: Mass Defect, m = m1 – m2
Step 2: Energy, E = mc2
Solution
Step 1
m = m1 – m2 = 5.02 x 10-27 – 5.01 x 10-27 = 1.0 x 10-29 kg
Step 2
The energy released, E = mc2 = 1.0 x 10-29 x (3 x 108)2 = 9.0 x 10-13 J
Therefore, the energy released is 9.0 x 10-13 joules
Problem 3
In the fusion of hydrogen isotopes into helium, the decrease in mass is about 0.65%. Calculate the energy obtainable when 1.0 grams of hydrogen is used.
Answer
The final answer to the above question is 5.85 x 1011 J
Explanation
Data
Since 1.0 g of hydrogen is used, we can start by converting grams into kilograms
1.0 g = 1.0/1000 = 0.001 kg
Also, mass defect, m = (0.65 / 100) x 0.001 = 6.5 x 106 kg
Speed of light, c = 3 x 108 m/s
Unknown
Energy, E = ?
Formula
E = mc2
Solution
E = mc2 = 6.5 x 106 x (3 x 108)2 = 5.85 x 1011 J
Therefore, the energy obtainable is 5.85 x 1011 joules
Problem 4
A possible fusion reaction is 12H + 12H —> 13H + 11H + Q, where Q is the energy released as a result of the reaction. If Q = 4.03 MeV, calculate the atomic mass of 13H in atomic mass units. [ 12H = 2.0141u; 11H = 1.00783u; 1u = 931 MeV ].
Answer
The final answer to the above question is 3.01604 u
Explanation
12H + 12H —> 13H + 11H + Q
Let x be the atomic mass of 13H in u
1 u = 931 MeV
Therefore, 4.03 MeV = 4.03 u / 931 = 0.004329 u
Substitute given values into the nuclear equation to obtain
2.01410 + 2.01410 —> x + 1.00783 + 0.0004329
4.0282 = x + 1.01216
x = 4.0282 – 1.01216 = 3.01604 u
Problem 5
The radioactive nuclei 84210Po emit an α-particle to produce 82206Pb. Calculate the energy in MeV released in each disintegration.
[ Take the masses of 84210Po = 209.936730 u; 82206Pb = 205.929421 u; 24He = 4.001504, and that 1 u = 931 MeV]
Answer
The final answer to the above question is Q = 5.404 MeV
Explanation
84210Po —> 24H + 82206H + Energy (Q)
1 u = 931 MeV
When we insert our values into the above nuclear reaction, we will have
(209.9367300) x 931 = (4.001504 + 205.929421) x 931 + Q
When we make Q subject of the formula, we will end up with
Q = 195451.0956 – 195445.6912 = 5.404 MeV
Problem 6
What is the binding energy of helium 24He
[Atomic mass of proton = 1.00783 u, the atomic mass of neutron = 1.00867 u]
Answer
The final answer to the above question is 0.033 u
Explanation
Data
Atomic energy of proton = 1.00783 u
The atomic mass of neutron = 1.00867 u
Also, the atomic mass of 2He = 4 u
Now, the number of protons = 2
The number of neutrons = 4 – 2 = 2
Mass of protons = 2 (1.00783 u) = 2.01566 u
Mass of neutrons = 2 (1.00867 u) = 2.01734 u
The total mass of neutron = 2.01566 + 2.01734 = 4.033 u
Therefore,
Binding energy = Difference between the mass of nucleon and that of nucleus = mass of nucleon – mass of the nucleus
The above expression will become
E = 4.033 u – 4 u = 0.003 u
Problem 7
The mass of a proton is 1.0074 u and that of a neutron is 1.0089 u. Determine the energy evolved in stabilizing the nucleus of nitrogen of a mass number 14 with 7 protons and 7 neutrons. [ Take the speed of light, c = 3 x 108 m/s; 1 u = 1.67 x 10-27 kg ]
Answer
The final answer to the above question is 1.715 x 10-11 J
Explanation
Data
Mass of proton = 1.0074 u
The mass of the neutron = 1.0089 u
Additionally, we have the mass of the nucleus = 14 u
Speed of light, c = 3 x 108 m/s
The number of protons = 7
Number of neutron = 7
We also have 1 u = 1.67 x 10-27 kg
To find the mass of the protons, we say
Mass of the protons = 7 x 1.0074 = 7.0518 u
The mass of neutrons = 7 x 1.0089 = 7.0623 u
Total mass of nucleon = mass of proton + mass of neutron = 7.0518 + 7.0623 = 14.1141 u
The mass of the nucleon in kg = 14.1141 x 1.67 x 10-27 = 2.3570547 x 10-26 kg
Mass of the nucleus in kg = 14 x 1.67 x 10-27 kg
Therefore, the mass defect, m = mass of nucleon – mass of nucleus = 2.3570547 x 10-26 – 2.338 x 10-26
m = 1.90547 x 10-28 kg
Energy evolved, E = mc2 = 1.90547 x 10-28 x (3.0 x 108)2 = 1.715 x 10-11 J
Problem 8
Calculate in Joules the binding energy for 94Be
[Take the atomic mass of 94Be = 9.01219 u; mass of the proton = 1.00783 u, mass of the neutron = 1.00867 u; unified atomic mass unit, u = 931 MeV; 1eV = 1.6 x 10-19 J]
Answer
The final answer to the above question is 9.3 x 10-12 J
Explanation
Number of protons = 4
The number of neutrons = 9 – 4 = 5
Mass of the protons = 4 (1.00783) = 4.03132 u
The mass of the neutrons = 5 (1.00867) = 5.04335 u
Hence,
Mass of the nucleon = mass of the proton + mass of the neutron = 4.03132 + 5.04335 = 9.07467 u
Now, we will calculate the mass defect
Mass defect = mass of nucleon – mass of nucleus = 9.07467 – 9.01219 = 0.06248 u
Therefore,
The binding energy = 0.06248 x 931 x 106 x 1.6 x 10-19 = 9.3 x 10-12 J
Problem 9
Deuteron and tritium fused to form a helium nucleus according to the equation.
21He + 31He —> 42He + 10n + Q
Calculate in Joules the energy released.
[31He = 3.01605 u; 21He = 2.0141 u; 42He = 4.00260 u; 10n = 1.00867 u; 1 u = 931 MeV, and 1 eV = 1.6 x 10-19 J ]
Answer
The final answer to the above question is Q = 2.812 x 10-12 J
Explanation
Total mass of the reactants = 2.01410 + 3.01605 = 5.03015 u
The total mass of products = 4.00260 + 1.00867 = 5.01127 u
Subsequently, our mass defect will become
Mass defect = mass of the reactant – mass of the product = 5.03015 – 5.01127 = 0.01888 u
Therefore, the energy released Q is
Q = 0.01888 x 931 x 1.6 x 10-19
The above expression will now become
Q = 2.812 x 10-12 Joules
Finally, the above-solved problems should help you to understand how to calculate binding energy. Feel free to reach out if you have more questions.
You may also like to read:
Mechanical Energy: Definition and Types