What is Kinetic Energy?
Definition of Kinetic Energy: The kinetic energy of a body can be defined as the energy of the body due to motion. The symbol for kinetic energy is KE. We measure kinetic energy in Joules (J). Kinetic energy is a scalar quantity.
Fundamental Concepts: At its core, kinetic energy is the energy an object possesses due to its motion. This energy is a result of an object’s mass and velocity. In simpler terms, the faster an object is moving and the more massive it is, the greater its kinetic energy. The formula to calculate kinetic energy is:
The formula for calculating kinetic is KE = (1/2)mv2
Where:
- KE represents kinetic energy.
- m is the mass of the object.
- v is the velocity of the object.

Historical Overview: The concept of kinetic energy has a rich history. It dates back to the works of scientists like Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz and Sir Isaac Newton, who made significant contributions to the understanding of motion and energy.
Key Principles: Kinetic energy is intertwined with several key principles:
- Relationship with Velocity: Kinetic energy increases exponentially with the square of an object’s velocity. In other words, doubling the velocity quadruples the kinetic energy.
- Scalar vs. Vector Quantity: Kinetic energy is a scalar quantity, meaning it only has magnitude and no direction, unlike velocity, which is a vector quantity.
Calculating Kinetic Energy
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating KE: Calculating kinetic energy is straightforward using the formula mentioned earlier. Let’s walk through a step-by-step example:
First Step: Measure the mass of the object in kilograms.
Second Step: Measure the velocity of the object in meters per second.
Third Step: Plug the values into the kinetic energy formula and solve for KE.
Real-World Examples: To make this concept more tangible, let’s explore a few real-world examples of kinetic energy calculations:
Calculating KE of Moving Vehicles: Imagine you have a car with a mass of 1,500 kg traveling at a speed of 30 m/s. Applying the formula, you find the car has a kinetic energy of 675,000 Joules.
KE in Sports: In sports, kinetic energy plays a crucial role. Think about a soccer ball being kicked with different velocities; the faster it goes, the more kinetic energy it carries. This principle also applies in other sports, such as tennis, baseball, and golf.
Derivation of Kinetic Energy (K.E) Formula
Assuming an object of mass m in kilogram has an initial velocity of u in meters per second. The object attains a final velocity of v in meters per second through a distance s in meters. We can derive the kinetic energy formula by applying the third equation of motion, the Second newton’s law of motion, and the formula for work done.
Step 1
Let’s get to work, start by making acceleration a subject of the formula from the equation v2 = u2 + 2as
We have an equation that says v2 = u2 + 2as
When we take the initial velocity u to the left-hand side, the above equation becomes
v2 – u2 = 2as
We can now divide both sides by 2s to make a subject of the formula [ (v2 – u2)/2s= 2as/2s ] to obtain
a = (v2 – u2)/2s
Now, remember that second Newton’s law says the force, f = ma [where m = mass and a = acceleration]
Hence, plugin a = (v2 – u2)/2s into f = ma
Which implies that
f = m x [ (v2 – u2)/2s ]
Therefore, we can break the right-hand side into
f = (1/2s) x m x (v2 – u2)
Remember that the formula for work done is w = f x s [ where w = work done, f = force, and s = distance]
Step 2
Hence, we can substitute f in the equation w = f x s into f = (1/2s) x m x (v2 – u2) to obtain
K.E = (1/2s) x m x (v2 – u2) x s
and s will cancel each other to leave us with
K.E = (1/2) x m x (v2 – u2)
If the initial velocity is zero (0) we will end up with
K.E = (1/2) x m x (v2 – 0)
Which is
K.E = (1/2) mv2 or 0.5mv2
Units of Kinetic Energy (K.E)
The units of kinetic energy depend on what you are calculating, and the units are as follows:
- Joules
- Kilojoules
- Calories
- We also use Foot-pound as a unit of kinetic energy
- Other units for kinetic energy are watt-hour and electron volt
Solved Problems: How to Calculate Kinetic Energy
Here are a few solved problems on how to calculate kinetic energy to help improve your understanding of the topic:
Problem 1
A body of mass 5 kilograms is acted upon by a constant force of 10 newtons for 4 seconds. Calculate the kinetic energy gained by the body.

Solution
Data
mass, m = 5 kg
force, f = 10 N
Time, t = 4 s
K.E=?
The formula for calculating K.E is (1/2)mv2
But we don’t have v and we need to apply the above data to find it
When we read the question again, we will see that
Initial velocity, u = 0
acceleration, a =f/m [Because f = ma]
Thus, a = 10/5 = 2 ms-2
Now, plugin t= 4 s, u=0, and a=2 ms-2 into the equation v = u+at to obtain
v = 0 + 2 x 4 = 8 m/s
Hence,
K.E = (1/2) mv2 = 0.5 x 5 x 82 = 160 J
Therefore, the kinetic energy of the body is 160 Joules.
Problem 2
An express train of mass 500 kilograms is moving with a velocity of 180 kilometers per hour. What is the kinetic energy of the train?

Solution
Data
Mass of the train, m = 500 kilograms
Velocity of the train, v = 180 km/h = (180 x1000m)/ 60 x 60s = 180,000m/3,600s = 50 m/s
And the formula for calculating kinetic energy is K.E = (1/2) mv2
Hence, we substitute our data into the above formula
K.E = 0.5 x 500 x 502 = 625,000 Joules = 625 kJ
Therefore, the kinetic energy of the train is 625 kilojoules
Problem 3
A hydrogen molecule of mass 3.3 x 10-27 kilograms is moving with a velocity of 1.7 x103 m/s. Calculate its kinetic energy.
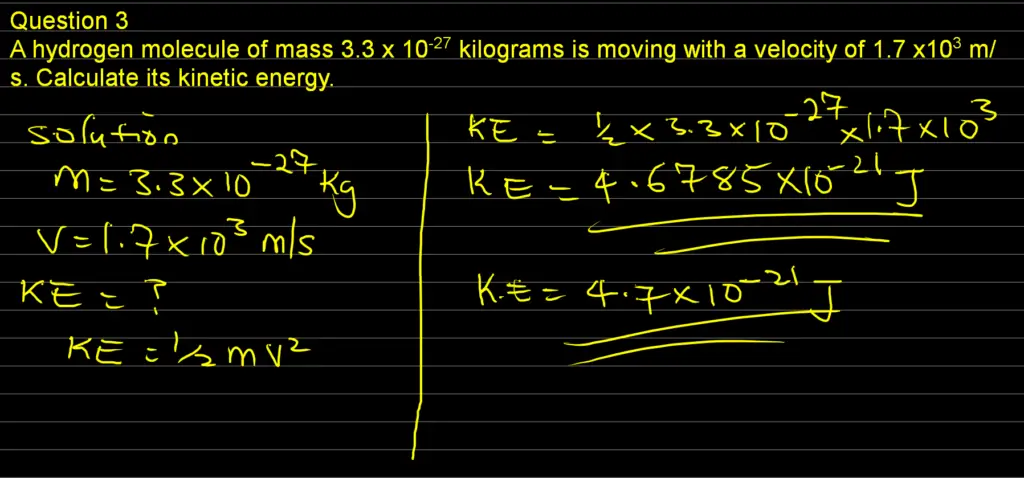
Solution
Data
Mass of the hydrogen, m = 3.3 x 10-27 kg
Velocity of hydrogen, v = 1.7 x 103 m/s
We can now apply the formula for K.E to solve the problem
K.E = (1/2) mv2
We can insert our data into the above formula to find the kinetic energy
K.E = 0.5 x 3.3 x 10-27 x (1.7 x 103)2
Which implies that K.E = 4.7685 x 10-21 Joules
Problem 4
A stone of mass 5 kilograms is thrown vertically upward with a velocity of 10m/s. Find the kinetic energy on reaching the ground.
Solution
Data
Extract your data from the question, it will make it easy for you to solve the problem.
Mass of the stone, m = 5 kg
velocity, v = 10 m/s
K.E =?
The formula for calculating kinetic energy is K.E = 0.5 mv2
Thus,
K.E = 0.5 x 5 x 102 = 2.5 x 100 = 250 J
Therefore, the kinetic energy is 250 Joules
Problem 5
A ball of mass 1000 grams is dropped from a height of 5 meters and rebounded to a height of 25 meters. Calculate the kinetic energy of the ball before impact.
Solution
Data
Mass of the ball, m = 1000 grams = 1 kg
height before impact = 5 meters
To find the velocity before impact, we need to understand that the ball is falling on the ground. Thus, we can apply the formula for potential energy
Potential energy (P.E) = mgh [ where m = mass, g = gravitational acceleration, and h = height]
We also know that K.E = P.E
Hence,
(1/2) mv2 = mgh
and m will cancel each other to give
(1/2) v2 = gh
But g is constant and is 9.8ms-2
Therefore,
v2 = 2gh = 2 x 9.8 x 5 = 98
Now, we can apply a square root to each side
v = √98 = 9.9 or 10 m/s which is the velocity before impact
Let’s insert our v above into the formula for kinetic energy
The kinetic energy is, K.E = 0.5 mv2 = 0.5 x 1 x 102 = 50 Joules
Problem 6
A body of mass 20 kilograms, initially at rest is subjected to a force of 40 newtons for one second. Calculate the change in kinetic energy.
Solution
Data
The change in kinetic energy is the same as the work done on the body.
Hence
Mass = 20 kg
The force f = 40 Newtons
Time, t = 1 Second
K.E = (1/2)mv2
and v = u + at [where a = acceleration and u = initial velocity]
u = 0 because the body was at rest
a = f/m = 40/20 = 2ms-2
Hence
v = 0 + 2 x 1 = 2 m/s
Therefore,
K.E = 0.5 x 20 x 22 = 10 x 4 = 40 J
Therefore, the kinetic energy of the body is 40 Joules
Problem 7
A body of mass 0.6 kg is thrown vertically upward from the ground with a speed of 20 m/s. Calculate its kinetic energy just before it hits the ground.
Solution
Data
Mass of the body, m = 0.6 kg
Velocity, v = 20 m/s
K.E =?
We can now apply the formula for kinetic energy which is K.E=(1/2)mv2 to solve the problem
After inserting our data into the above formula. We will get
K.E = 0.5 x 0.6 x 202 = 0.3 x 400 = 120 J
Therefore the kinetic energy before hitting the ground is 120 Joules
Problem 8
A body of mass 5 kilograms falls from a height of 10 meters above the ground. What is the kinetic energy of the body just before it strikes the ground?
[Neglect energy losses and take g = 10 m/s2]
Solution
Data
Mass of the body, m = 5 kg
height is the distance, s = 10 m
K.E = (1/2)mv2
But we need to find v
Let us apply one of the equations of motion (v2 = u2 + 2as) to find v
After inserting our data into the above equation of motion, we will have
v2 = 02 + 2 x 9.8 x 10 [ Where a=g=10m/s2 and u=initial velocity= 0 because the body starts from rest]
v = √ 196 =14 m/s
Now we can apply the formula for kinetic energy
K.E = (1/2)mv2 = 0.5 x 5 x 142 = 490 Joules
Problem 9
A bus of mass 800 kilograms is traveling at a speed of 5 m/s. Determine the kinetic energy of the bus.
Solution
Data
Mass of the bus, m = 800 kg
Speed of the bus, v = 5 m/s
K.E =?
Apply the formula below to solve the problem
K.E = (1/2)mv2
Substitute the equations above with our data
K.E = 0.5 x 800 x 52 = 400 x 25 = 10,000 J = 10 kJ
Therefore, the kinetic energy of the bus is 10 kilojoules
Problem 10
A ball of mass 0.7 kilograms is thrown at a speed of 10 m/s. Calculate the kinetic energy of the ball
Solution
Data
Mass of the ball, m = 0.7 kg
Speed of the ball, v = 10 m/s
K.E =?
Solve the problem by applying K.E=(1/2)mv2
K.E = 0.5 x 0.7 x 102 = 0.35 x 100 = 35 J
Therefore, the kinetic energy of the ball is 35 Joules
Other Forms of Energy that Involve Kinetic Energy?
Kinetic energy can be:
- Mechanical
- Thermal
- In the form of Sound
- Electrical or
- Radiation
Applications of Kinetic Energy
- To generate electricity
- Sailor working on the boat
- Firing a bullet
- Sending a rocket from one planet to another
Important Points on Kinetic Energy
- The energy is due to motion
- The energy is a horizontal energy
- Kinetic energy does not act against gravity
- The symbol of Kinetic energy is K.E or KE
The Conservation of Kinetic Energy
Overview of Conservation Laws: One of the remarkable aspects of kinetic energy is its conservation under specific conditions. The principle of conservation of energy states that the total energy in a closed system remains constant. In simpler terms, if no external forces are acting on an object, its total energy, including kinetic energy, remains unchanged.
Examples of KE Conservation: Two common scenarios where kinetic energy conservation is observed are:
Collisions: In a perfectly elastic collision between two objects, the total kinetic energy of the system is conserved. For instance, in a game of billiards, the kinetic energy of the cue ball is transferred to the other balls, and the total KE remains the same.
Pendulum Motion: In a swinging pendulum, kinetic energy is continually converted to potential energy as the pendulum moves upward and vice versa. The total mechanical energy (sum of kinetic and potential energy) remains constant.
Factors Affecting Kinetic Energy
Mass and Velocity: The relationship between mass and kinetic energy is direct; as mass increases, kinetic energy also increases. However, velocity has a more significant impact on KE. Even a small increase in velocity results in a substantial increase in kinetic energy due to the quadratic relationship.
Impact of Air Resistance: In the real world, objects moving through a fluid, like air, experience resistance. Air resistance opposes the motion of an object, and as a result, some kinetic energy is transformed into other forms of energy, like thermal energy. This phenomenon is why objects eventually come to a stop if no additional force is applied.
Practical Examples: Consider the following practical examples that showcase the influence of mass, velocity, and air resistance on kinetic energy:
High-Speed Vehicles: Suppose you have two cars of the same mass, but one is moving at 100 mph while the other is moving at 50 mph. The faster car has four times the kinetic energy of the slower one, emphasizing the significance of velocity.
Skydiving: During a skydive, you accelerate due to gravity. As you gain speed, your kinetic energy increases. However, as you deploy your parachute and air resistance comes into play, your kinetic energy decreases, allowing for a safe descent.
Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy
Relationship between KE and PE: In many systems, kinetic energy and potential energy are interconnected. Potential energy is the energy an object possesses due to its position or height relative to a reference point, while kinetic energy is associated with motion.
Conversion between the Two: Objects can convert between kinetic and potential energy. For example, when you throw a ball upwards, it initially has high kinetic energy and low potential energy. As it rises, its kinetic energy decreases while its potential energy increases. At the highest point of its trajectory, the kinetic energy is minimal, and potential energy is at its peak.
Applications in Engineering: The interplay between kinetic and potential energy is harnessed in various engineering applications:
Roller Coasters: Roller coasters are a prime example of kinetic and potential energy conversion. As the coaster climbs the initial hill, potential energy increases. When it descends, potential energy is converted back into kinetic energy, providing thrills to riders.
Renewable Energy: Hydropower systems use the conversion between kinetic and potential energy in water to generate electricity. Falling water turns turbines, converting gravitational potential energy into electrical energy.
Kinetic Energy in the Universe
Celestial Bodies and KE: Kinetic energy is a fundamental concept in understanding the motion of celestial bodies within our universe. Some noteworthy examples include:
Earth’s Orbit: The Earth’s kinetic energy is responsible for its orbital motion around the Sun. This kinetic energy prevents the Earth from spiraling into the Sun.
Solar System: In the solar system, each planet possesses kinetic energy due to its motion around the Sun. The differences in mass and velocity between planets result in varying amounts of kinetic energy.
Cosmic Phenomena: In the vast expanse of the universe, kinetic energy plays a role in various cosmic phenomena:
Supernovae: The explosive death of massive stars, known as supernovae, releases an immense amount of energy, primarily in the form of kinetic energy. The ejected materials from the star’s core carry this energy into space.
Galactic Motion: Galaxies themselves are in constant motion. The kinetic energy of galaxies contributes to the structure and dynamics of the universe on a cosmic scale.
Applications of Kinetic Energy
Energy Generation: Kinetic energy has practical applications in energy generation:
Wind Turbines: Wind turbines harness the kinetic energy of moving air to generate electricity. As wind flows over the blades, it causes them to rotate, converting kinetic energy into electrical energy.
Hydroelectric Power: Hydroelectric power plants use the kinetic energy of flowing water to turn turbines, producing electricity. The greater the flow of water, the higher the kinetic energy, leading to more power generation.
Transportation: The transportation industry relies heavily on kinetic energy:
Electric Vehicles: Electric cars utilize stored electrical energy to accelerate and gain kinetic energy. Their efficiency in converting this energy into motion is a key factor in their success.
High-Speed Trains: High-speed trains like the Shinkansen in Japan exemplify the efficient use of kinetic energy for rapid transportation. These trains can reach remarkable speeds thanks to their kinetic energy.
Safety and Kinetic Energy
Understanding Impact and Injury: In our daily lives, understanding kinetic energy is crucial for safety. In scenarios involving impacts, such as car accidents or sports collisions, knowing the potential energy involved helps engineers design safety measures.
Safety Measures: Several safety measures are employed to mitigate the risks associated with high kinetic energy:
Vehicle Safety: Modern cars are equipped with various safety features, including airbags, crumple zones, and seat belts, designed to absorb and dissipate kinetic energy in the event of a collision, thereby protecting passengers.
Sports Equipment: In sports like football and hockey, helmets and padding are used to reduce the impact of kinetic energy during collisions, minimizing the risk of injury.
Fun Facts and Trivia
Unusual Uses of KE: While kinetic energy is a fundamental concept, it also finds its way into unexpected and fascinating applications:
Wind-Powered Art: Some artists create kinetic sculptures that move gracefully with the wind, demonstrating the beauty of kinetic energy in art.
KE Records: Throughout history, there have been remarkable records related to kinetic energy:
Fastest Man-Made Object: The Parker Solar Probe, a NASA spacecraft, holds the record for the fastest man-made object, achieving speeds of up to 700,000 kilometers per hour to study the Sun.
Conclusion
In conclusion, kinetic energy is a fundamental concept in physics that influences our daily lives, from the cars we drive to the sports we play. Its conservation and conversion principles are essential for understanding various natural phenomena, from the orbits of planets to the motion of galaxies in the universe. Moreover, kinetic energy plays a critical role in generating renewable energy and ensuring safety in transportation and sports.
As you continue to explore the world around you, keep in mind the profound impact of kinetic energy. Whether you’re watching a thrilling roller coaster ride or witnessing the beauty of celestial bodies in the night sky, the concept of kinetic energy will always be at the heart of the action, providing both wonder and understanding.
References and External Links
To further enhance your understanding of kinetic energy, we recommend exploring the following authoritative sources and websites:
- NASA – Understanding Kinetic and Potential Energy
- The Physics Classroom – Kinetic Energy
- Khan Academy – Kinetic Energy
- Physics LibreTexts – Kinetic Energy
- National Renewable Energy Laboratory – Wind Energy Basics
These sources provide in-depth insights into kinetic energy, its applications, and related concepts.
You may also like to read:
How to Calculate Kinetic Energy Without Velocity
Mechanical Energy: Definition and Types
How to Calculate Work Done in Physics
Sources: