What is Boyle’s Law?
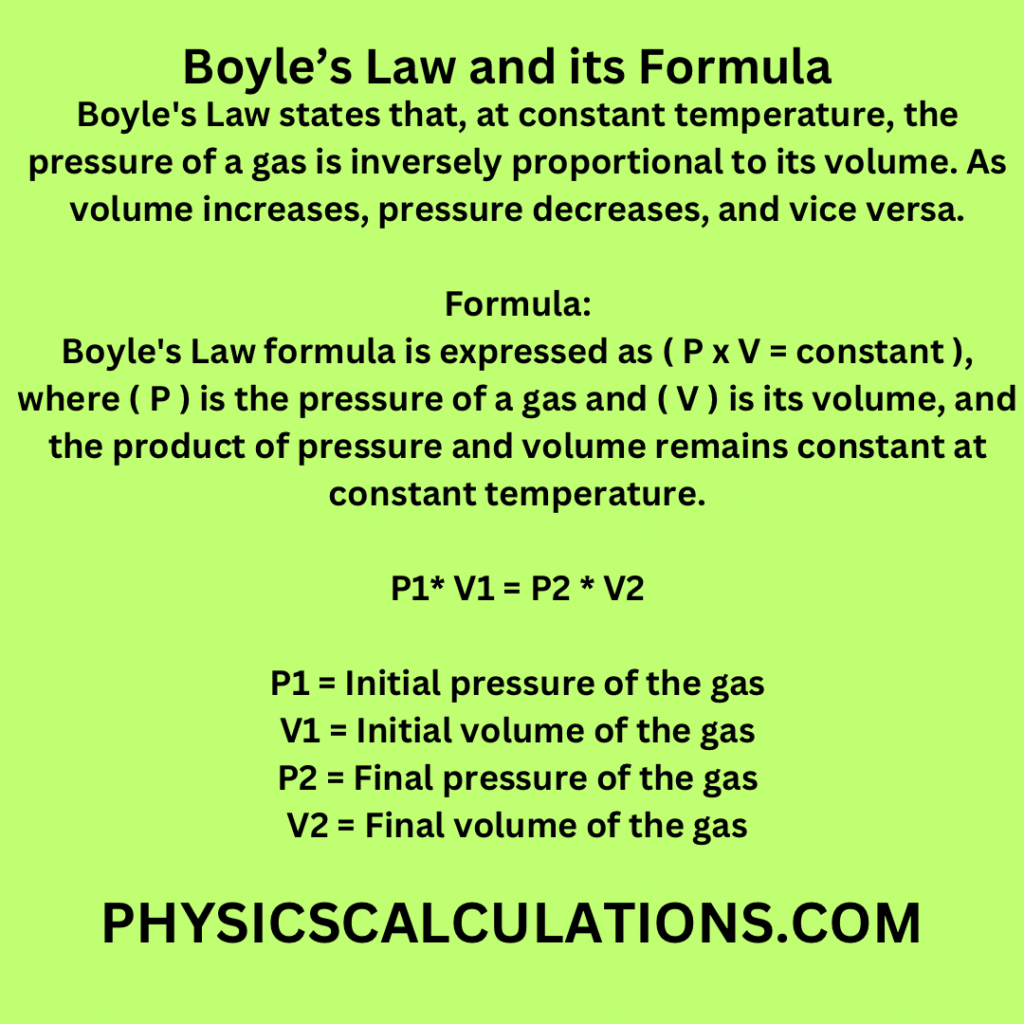
Boyle’s Law states that, at constant temperature, the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume. As volume increases, pressure decreases, and vice versa.
Boyle’s Law formula is expressed as ( P x V = constant ), where ( P ) is the pressure of a gas and ( V ) is its volume, and the product of pressure and volume remains constant at constant temperature.
Boyle’s Law: Explanation
The Boyle’s Law is a fundamental gas law that states the inverse relationship between the pressure and volume of a given amount of gas, provided the temperature remains constant. In simple terms, as the pressure exerted on a gas increases, its volume decreases, and vice versa.
Now, let us talk about Boyle’s Law in a way that’s easy to understand. Imagine you have a balloon, and you are going to find out what happens when you squish it or let it expand.
Boyle’s Law:
Boyle’s Law is like a magical rule for balloons. It helps us understand what happens when we change the pressure and size of a balloon, but we keep the temperature the same. So, if you squeeze a balloon, what happens to its pressure and size?
Balloon Experiment:
Picture a balloon at room temperature, not too hot or cold. Now, if you gently squeeze the balloon, you’ll notice it gets smaller. Boyle’s Law helps us understand this! It says that when you change the pressure on a balloon, the size of the balloon changes too.
Simple Idea:
Think of the gas inside the balloon as a bunch of tiny, bouncy balls. When you squeeze the balloon, you’re pushing those balls closer together. When they’re closer, the balloon gets smaller. So, Boyle’s Law is like saying, “When you squish a balloon, its size goes down.”
Formula (Kind of):
Now, if we want to sound a bit like scientists, Boyle’s Law can be written as ( P x V = constant), where (P) is pressure, (V) is volume, and their product stays the same when you squish or expand the balloon.
In simpler terms, Boyle’s Law helps us figure out what happens to a balloon when we change how much we squeeze it or let it expand while keeping the temperature the same. It’s like learning about the magic of balloons and how they react to pressure changes!
The History of Boyle’s Law
Boyle’s Law has a rich historical background that dates back to the 17th century. Let’s take a brief journey through its origin and development.
The Discoverer: Robert Boyle
Robert Boyle, an Irish natural philosopher, chemist, and physicist, is credited with the discovery of Boyle’s Law. In 1662, he published “The Sceptical Chymist,” a groundbreaking work that laid the foundation for modern chemistry and introduced the world to Boyle’s Law.
Predecessors of Boyle’s Law
Before Boyle’s groundbreaking work, several scientists and philosophers contributed to the understanding of gas behavior. Among them were Evangelista Torricelli, Galileo Galilei, and Edme Mariotte, whose collective insights paved the way for Boyle’s Law.
Experimental Evidence
Boyle conducted a series of meticulous experiments using a J-shaped glass tube filled with mercury, now known as the “Boyle’s Tube.” By varying the pressure and measuring the corresponding volume changes, he established the empirical evidence supporting his law.
The Mathematical Expression of Boyle’s Law
Mathematically, Boyle’s Law equation can be expressed as follows:
P1* V1 = P2 * V2
Where:
- P1 = Initial pressure of the gas
- V1 = Initial volume of the gas
- P2 = Final pressure of the gas
- V2 = Final volume of the gas
Real-Life Applications of Boyle’s Law
Boyle’s Law finds applications in numerous fields, significantly impacting our daily lives. Let’s explore some of the most notable applications:
1. Scuba Diving
The principles of Boyle’s Law plays a key role in scuba diving. As divers descend into deeper waters, the pressure increases, causing the volume of the air in their scuba tanks to decrease. Understanding this relationship is essential for safe and successful dives.
2. Medical Ventilators
Medical ventilators, used to assist patients with breathing difficulties, rely on Boyle’s Law to regulate air pressure and volume during the breathing cycle.
3. Aerosol Cans
Aerosol cans, such as spray paints and deodorants, utilize Boyle’s Law to dispense their contents. When the valve is opened, the pressure inside the can decreases, allowing the contents to be released.
4. Weather Balloons
Boyle’s Law plays a crucial role in weather balloons, which change volume as they ascend or descend through the atmosphere due to varying air pressure.
5. Lung Function Testing
Pulmonary function tests in medicine employ Boyle’s Law principles to assess lung function and diagnose respiratory conditions.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- What is Boyle’s Law?
Boyle’s Law states the inverse relationship between pressure and volume in a gas when the temperature remains constant. - Who discovered Boyle’s Law?
The law was discovered by Robert Boyle, an Irish natural philosopher, chemist, and physicist, in the 17th century. - What is the mathematical expression of Boyle’s Law?
The mathematical expression of Boyle’s Law is given by the equation: P1 * V1 = P2 * V2. - How is Boyle’s Law applied in scuba diving?
In scuba diving, as divers descend into deeper waters, the pressure increases, causing the volume of the air in their scuba tanks to decrease, following Boyle’s Law. - What are some real-life applications of Boyle’s Law?
Boyle’s Law finds applications in various fields, including scuba diving, medical ventilators, aerosol cans, weather balloons, and lung function testing. - How does Boyle’s Law impact weather balloons?
Weather balloons change volume as they ascend or descend through the atmosphere due to varying air pressure, in accordance with Boyle’s Law.
Conclusion
Boyle’s Law is a fundamental concept in physics, providing invaluable insights into the relationship between pressure and volume in gases. Its real-life applications span various industries, impacting our lives in more ways than we might realize. Understanding this law helps us harness its principles for innovation, safety, and technological advancements.
So, the next time you use an aerosol can, go scuba diving, or undergo a lung function test, remember that Boyle’s Law is at work, shaping the world around us.
You may also like to read: